
What we need for this tutorial
- A Latest Windows (if you have ubuntu installed skip to the commands part)
- WSL or WSL2
- Ubuntu Subsystem installed from the Windows store.
Installing WSL on Windows
To install the WSL(Windows Subsystem for Linux) on Windows, you need to make sure that you’re running latest version of Windows.
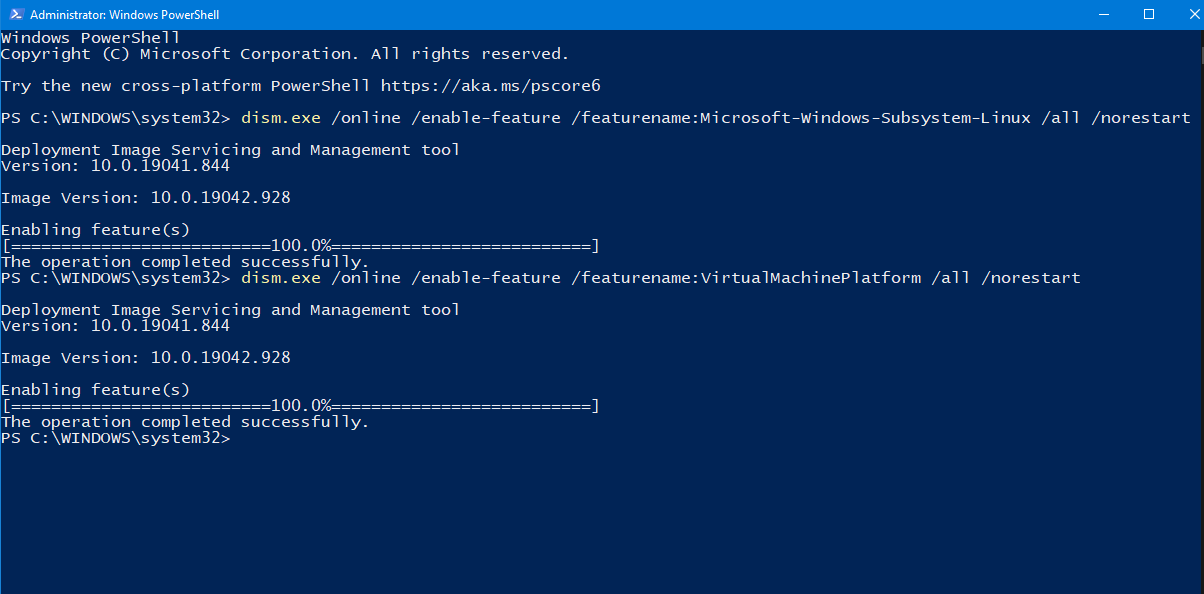
Install WSL by opening powershell with admin priviledges and typing this command.
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux /all /norestart
This command will enable WSL Feature on Windows. You can restart your system now and skip next step.
Upgrading to WSL2
In this tutorial, We are gonna install WSL2, so Extra steps will be needed.
To enable WSL2, You need to enable another feature by typing this command in powershell window with admin priviledges.
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestart
After enabling this feature, RESTART your System.
Now download wsl2 package from this link, Download From Here and Install it.
Now, Let’s set wsl default version to 2 by typing this command in powershell with admin priviledges.
wsl --set-default-version 2
Now WSL2 is now installed on our sytem.
Installing Linux Distribution
In this tutorial, I’m gonna install Ubuntu (You can install other linux as well). Go to Microsoft Store and download Ubuntu.
I’m also going to install Windows Termnial. You can download this from Windows store too.
 After Downloading, Launch it. It will ask for creating a new user.
After Downloading, Launch it. It will ask for creating a new user.
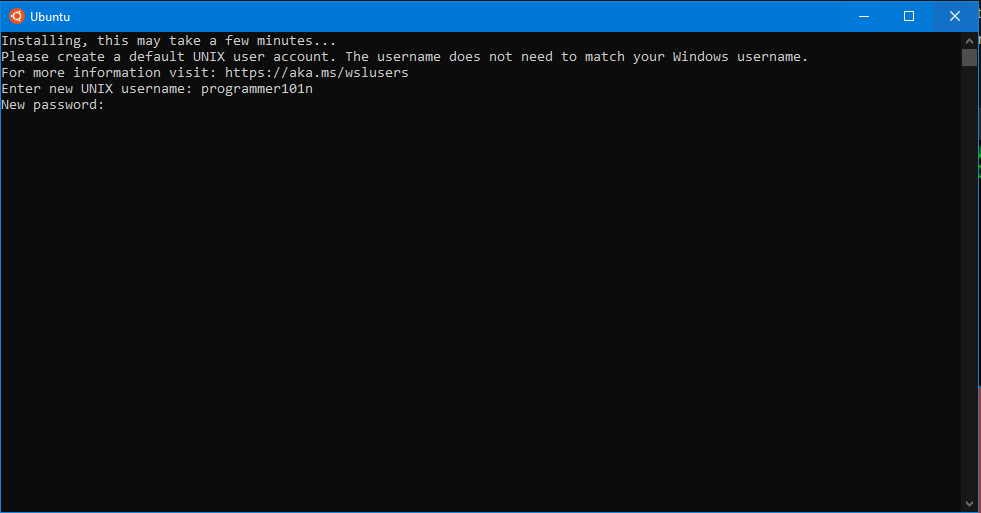
Now you have successfully installed the Ubuntu on Windows.
Basic of Linux Commands
First we need to discuss some things that will be used to explain below.
-
: This denotes that the variable name is required or absolutely neccessary to give. -
- [args]
- This denotes that the args are optional or you can leave it empty
Now let’s dive into commands.
-
User Commands
-
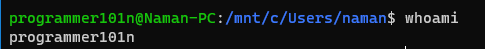
- whoami
- returns your username
-
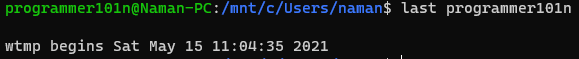
- last [username]
- prints the last login of the username or current logged in user.
-
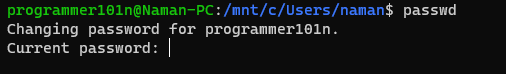
- passwd
- Change the password of the current logged in user.
-
-
Date and Time
-
- date [+format_string]
- Returns the current date and time.

-
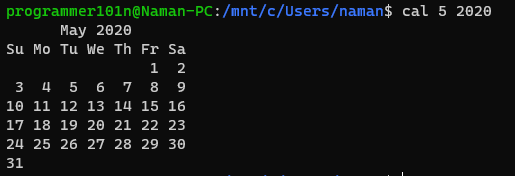
- cal [month] [year]
- Shows the current or specified calendar of the month and year.
-
-
Files and Directories
-
- cd <directory>
- To change the current working directory.
-
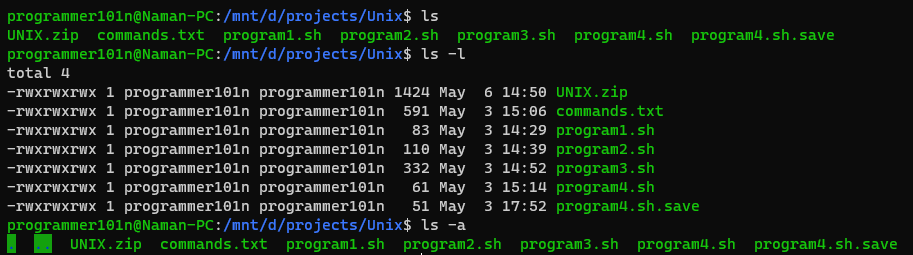
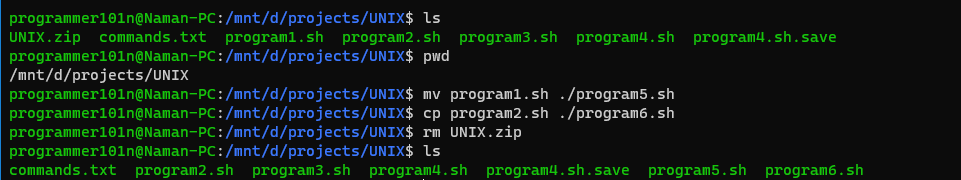
- ls [-l] [-a]
- Shows all files in your directory, -l paramater shows the files in long format, -a paramter shows the hidden files too.
-
- pwd
- Prints the current working directory.
-
- mv <filename1> <filename2>
- Moves the file from one directory to another.
-
- cp <filename1> <filename2>
- Copies the file from one directory to another.
-
- rm <filename>
- Removes the file from directory.
-
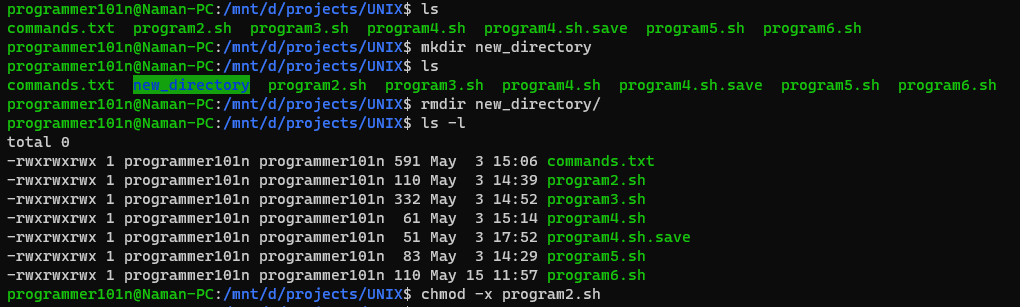
- mkdir <directoryname>
- Create new Directory with directoryname
-
- rmdir <directoryname> [-r]
- Removes the Directory with directoryname, -r parameter to recursive delete
-
- chmod <options> <filename>
- Lets you change the read, write, and execute permissions on your files.
-
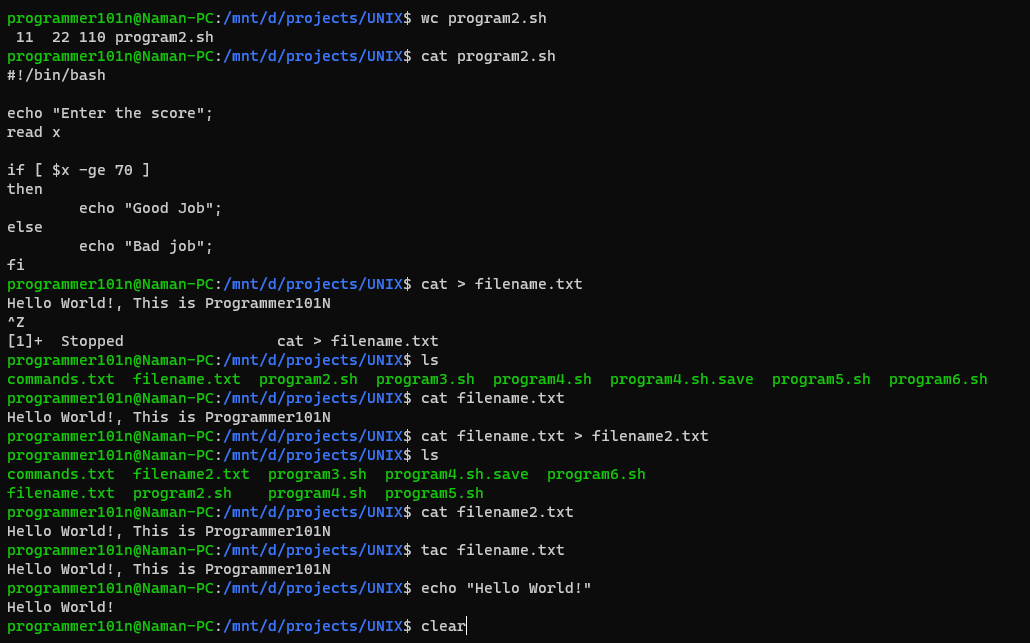
- wc <filename>
- Print the line, words and characters count in the file.

-
-
Creating and reading the file
-
- cat <filename>
- Prints the contents of the file .
-
- cat > filename
- Creates a file with entered content.
-
- cat <filename1> <filename2> … > filename
- Copy the contents from filename1, filename2 … to filename.
-
- tac <filename>
- Prints the contents of the file in reverse.
-
- echo <message>
- Prints or Broadcast the message on the terminal.
-
- clear
- Clear the terminal.
-
This is all the basic commands of the linux system. Stay tuned for more updates.
